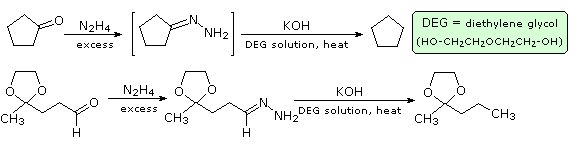
Wolff-Kishner Reduction
Reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with excess hydrazine generates a hydrazone derivative, which on heating with base gives the corresponding hydrocarbon. A high-boiling hydroxylic solvent, such as diethylene glycol, is commonly used to achieve the temperatures needed. The following diagram shows how this reduction may be used to convert cyclopentanone to cyclopentane. A second example, in which an aldehyde is similarly reduced to a methyl group, also illustrates again the use of an acetal protective group. The mechanism of this useful transformation involves tautomerization of the initially formed hydrazone to an azo isomer.
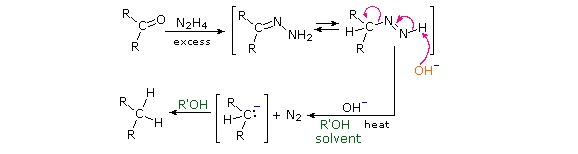
Mechanism

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.